HAND PROCEDURES
Trigger Finger
What is it?
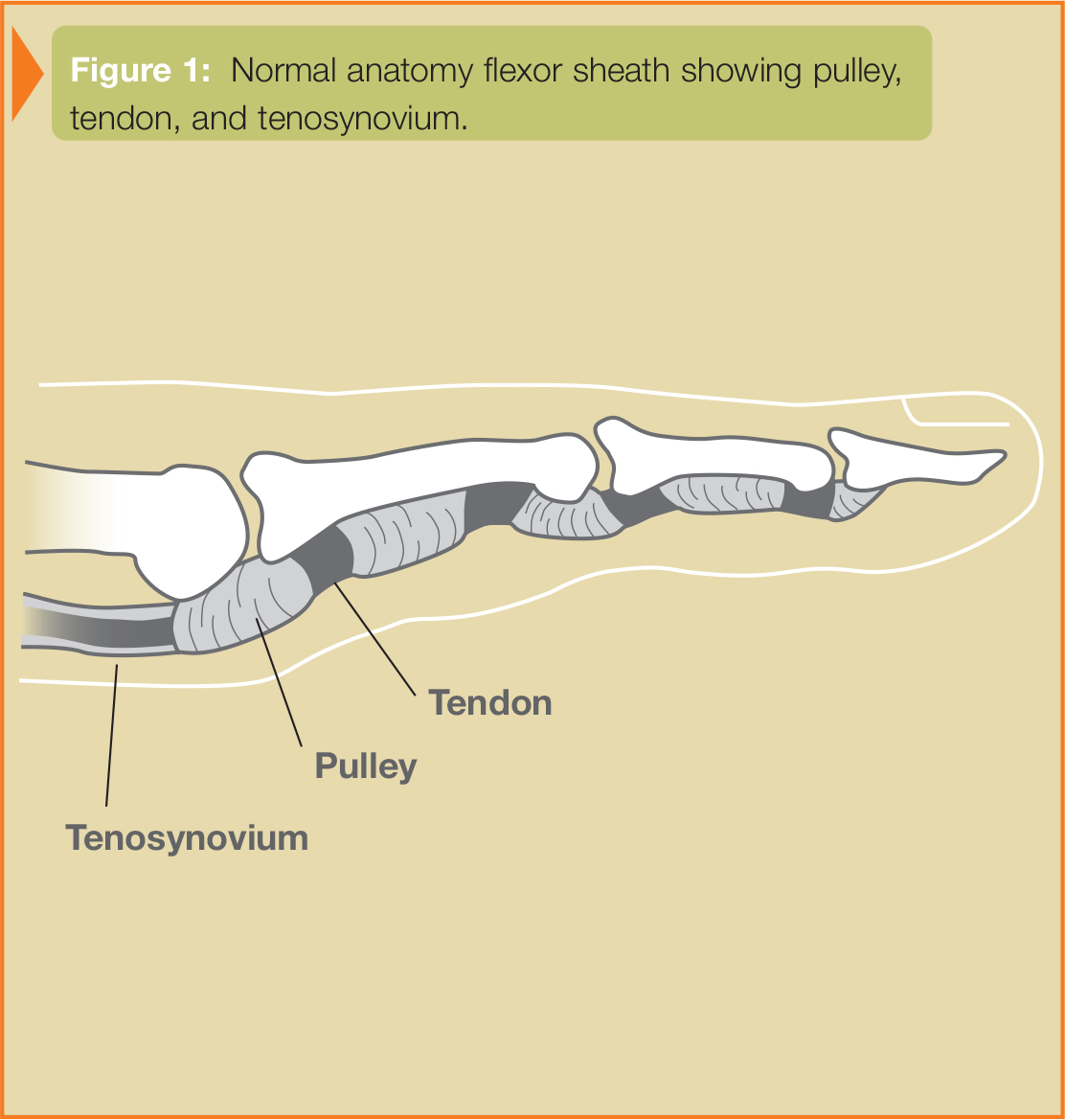
Stenosing tenosynovitis, commonly known as “trigger finger” or “trigger thumb”, involves the pulleys and tendons in the hand that bend the fingers. The tendons work like long ropes connecting the muscles of the forearm with the bones of the fingers and thumb. In the finger, the pulleys are a series of rings that form a tunnel through which the tendons must glide, much like the guides on a fishing rod through which the line (or tendon) must pass. These pulleys hold the tendons close against the bone. The tendons and the tunnel have a slick lining that allows easy gliding of the tendon through the pulleys (see Figure 1).
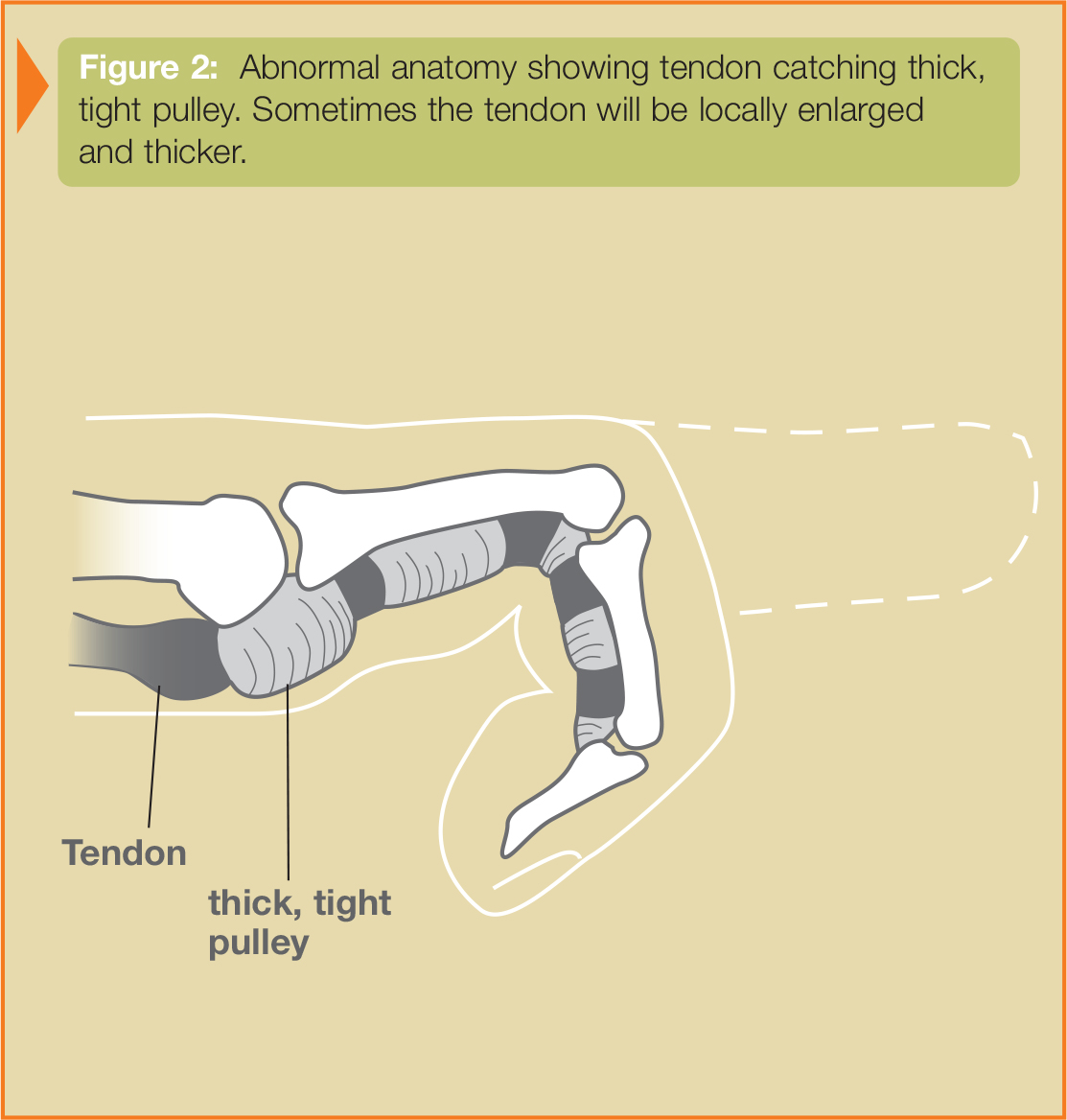
Trigger finger/thumb occurs when the pulley at the base of the finger becomes too thick and constricting around the tendon, making it hard for the tendon to move freely through the pulley. Sometimes the tendon develops a nodule (knot) or swelling of its lining. Because of the increased resistance to the gliding of the tendon through the pulley, one may feel pain, popping, or a catching feeling in the finger or thumb (see Figure 2). When the tendon catches, it produces inflammation and more swelling. This causes a vicious cycle of triggering, inflammation, and swelling. Sometimes the finger becomes stuck or locked, and is hard to straighten or bend.
What causes it?
Causes for this condition are not always clear. Some trigger fingers are associated with medical conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis, gout, and diabetes. Local trauma to the palm/base of the finger may be a factor on occasion, but in most cases there is not a clear cause.
Signs and symptoms
Trigger finger/thumb may start with discomfort felt at the base of the finger or thumb, where they join the palm. This area is often tender to local pressure. A nodule may sometimes be found in this area. When the finger begins to trigger or lock, the patient may think the problem is at the middle knuckle of the finger or the tip knuckle of the thumb, since the tendon that is sticking is the one that moves these joints.
Treatment
The goal of treatment in trigger finger/thumb is to eliminate the catching or locking and allow full movement of the finger or thumb without discomfort Swelling around the flexor tendon and tendon sheath must be reduced to allow smooth gliding of the tendon. The wearing of a splint or taking an oral anti-inflammatory medication may sometimes help. Treatment may also include changing activities to reduce swelling. An injection of steroid into the area around the tendon and pulley is often effective in relieving the trigger finger/thumb. If non-surgical forms of treatment do not relieve the symptoms, surgery may be recommended. This surgery is performed as an outpatient, usually with simple local anesthesia. The goal of surgery is to open the pulley at the base of the finger so that the tendon can glide more freely. Active motion of the finger generally begins immediately after surgery. Normal use of the hand can usually be resumed once comfort permits. Some patients may feel tenderness, discomfort, and swelling about the area of their surgery longer than others. Occasionally, hand therapy is required after surgery to regain better use.